C Nested Loop
In c programming, loop within a loop is called a nested loop. In this tutorial, we will learn about nested loops in c programming with examples.
What Is Nested Loop
When there is a loop statement inside another loop statement then it is known as a nested loop statement. It is possible to have a loop statement as a part of another loop statement in c programming. There can be any number of loops inside a loop. It is not necessary that the loop must be nested inside the same type of loop. There can be any type of loop nested inside the body of another loop, such as a while loop or for a loop. For example, we can have an inner for loop inside the outer while loop.
Syntax:-
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
outer_loop { //Outer Loop Statements inner_loop { //Inner loop Statements } } |
How nested loop works
For every pass of the outer loop triggers the inner loop. This repeats until the outer loop completes all iterations. For each iteration of the outer loop inner loop execute all its iteration. It is possible to have a break statement within either the inner or outer loop to interrupt this process. A total number of iterations is equal to the number of iterations of the outer loop multiplied by the number of iterations in an inner loop.
Nested for Loop
When there is for loop inside another for loop statement then it is known as a nested for loop statement. It is possible to have a for loop statement as a part of another for loop statement. Below is the general syntax of nested for loop statements in c programming:
Syntax:-
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
for ( init; condition; increment ) { for ( init; condition; increment ) { statement(s); } statement(s); } |
Below is a simple example to demonstrate the use of nested for loop statement in c programming. In this example, we are using a for loop inside a for a loop.
Example:-
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
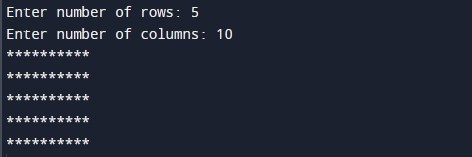
#include<stdio.h> void main() { int rows, cols,i, j; printf("Enter number of rows: "); scanf("%d", &rows); printf("Enter number of columns: "); scanf("%d", &cols); for(i = 1; i<=rows; i++) { for(j = 1; j <= cols; j++) { printf("*"); } printf("\n"); } } |
Output:-
Nested while Loop
When there is a while loop inside another while loop statement then it is known as a nested while loop statement. It is possible to have a while loop statement as a part of another while loop statement. Below is the general syntax of nested while loop statement in c programming:
Syntax:-
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
while(condition) { while(condition) { statement(s); } statement(s); } |
Below is a simple example to demonstrate the use of a nested while loop statement in c programming:
Example:-
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
#include<stdio.h> void main() { int rows, cols; int i=1; int j; printf("Enter number of rows: "); scanf("%d", &rows); printf("Enter number of columns: "); scanf("%d", &cols); while(i<=rows) { j = 1; while(j<=cols) { printf("*"); j = j+1; } printf("\n"); i = i+1; } } |
Output:-

Nested do-while Loop
When there is a do-while loop inside another do while loop statement then it is known as a nested do-while loop statement. It is possible to have a do-while loop statement as a part of another do while loop statement. Below is the general syntax of nested do…while loop statement in c programming:
Syntax:-
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
do { statement(s); do { statement(s); }while( condition ); }while( condition ); |
Below is a simple example to demonstrate the use of a nested do-while loop statement in c programming:
Example:-
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
#include<stdio.h> void main() { int rows, cols; int i=1; int j; printf("Enter number of rows: "); scanf("%d", &rows); printf("Enter number of columns: "); scanf("%d", &cols); do{ j = 1; do{ printf("*"); j = j+1; }while(j<=cols); printf("\n"); i = i+1; }while(i<=rows); } |
Output:-

When To Use a Nested Loop
Nested loops are handy when you want to loop through multi-dimensional data. For example, it is easy to traverse a multi-dimensional array using nested loops.
Break In Nested loop
The break statement is used to exit out of the loop. If the break statement is used inside a nested loop, it will terminate the innermost loop.
Continue In the Nested loop
The continue statement is used to skip the current iteration and move to the next iteration. When a continue statement is encountered inside a loop, it skips all the statements below it and jumps the control to the next iteration.