In this tutorial you will learn about the Java Decision Making Statements and its application with practical example.
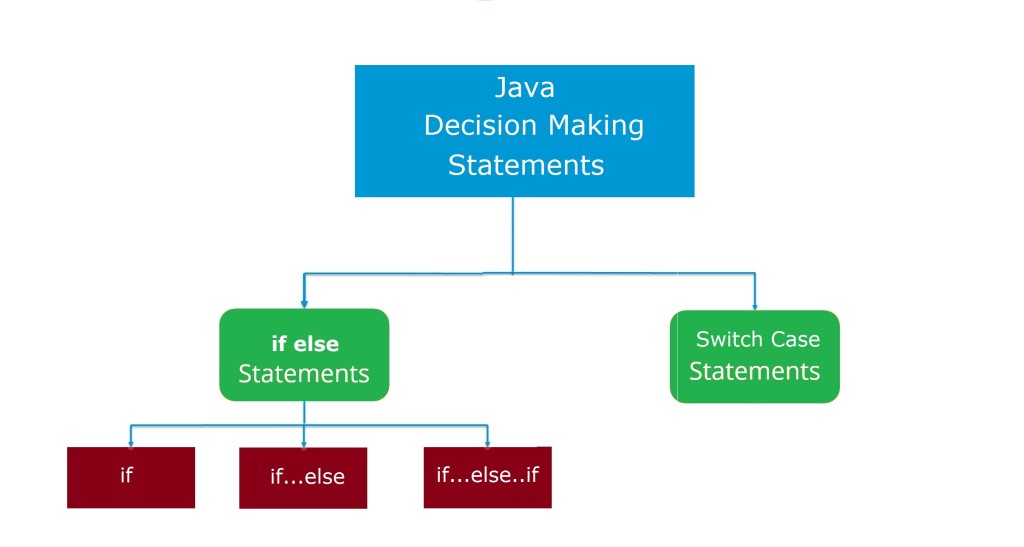
Java Decision Making Statements
There are cases where we want a block of code to be executed when some condition is satisfied. In Java, we have a rich set of decision-making statements that enable computer to decide which block of code to execute based on some conditional choices. Decision-making statement. A Decision-making statement evaluates single or multiple test expressions which result is “TRUE” or “FALSE”. The outcome of the test expression/condition helps to determine which block of the statement(s) to execute if the condition is “TRUE” or “FALSE” otherwise.
In Java, we have the following decision-making statements –
- Java if Statements
- Java If else Statements
- Java if else if Statements
- Java Nested If Statements
- Java Switch Case Statement
Java If Statement
If a statement allows a block of code to be executed only when a specified condition is true. An if statement evaluates a boolean expression followed by one or more statements. The given boolean expression results in a boolean value that can only be either true or false.
Syntax:-
|
1 2 3 |
if(condition){ // statements } |
Here, a condition is a Boolean expression that results in either True or False, if it results in True then statements inside the body is executed, if it results in False then execution is skipped from if body.
Java If Else Statement
In Java, when we want to execute a block of code when the if the condition is true and another block of code when the if the condition is false, In such a case we use the if…else statement.
Syntax:-
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
if(condition){ // statements } else { // statements } |
Here, a condition is a Boolean expression that results in either True or False, if it results in True then statements inside the body is executed, if it results in False then statements inside else body are executed.
Java If Else If Statement
When we want to add multiple condition checks in a single if-else statement then by using the if else-if else statement we can easily add multiple conditions. In Java, if..else…if statement allows us to add an alternative set of test conditions in the if..else statement using else-if and single else statements for the if condition. In such way if..else…if statement is used to select one among several blocks of code to be executed.
Syntax:-
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
if(condition1) { // statement(s) } else if(condition2){ // statement(s) } . . else if(conditionN){ // statement(s) } else { // statement(s) } |
Java Nested If Statement
In Java, when there is an if statement inside another if statement then it is known as nested if-else. Nested if-else can also be simplified using Java Switch Case Statement.
Syntax:-
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
if(condition1) { if(condition2){ // statements } else { // statements } } else { if(condition3){ // statements } else { // statements } } |
Java Switch Case Statement
In Java, a switch case statement is a simplified form of the Java Nested if-else statement, it helps to avoid a long chain of if..else if..else statements. A switch-case statement evaluates an expression against multiple cases in order to identify the block of code to be executed.
Syntax:-
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
switch(expression){ case value1: // statements break; case value2: // statements break; default: // statements break; } |