In this tutorial you will learn about the Sentence Factors and its application with practical example.
In this tutorial, we will learn about Sentence Factors
Prerequisites
Before starting with this tutorial we assume that you are best aware of the following topics:
- Nouns.
- Pronouns.
- Verbs.
- Adjectives.
- Adverbs.
- Prepositions.
- Conjunctions.
- Interjections.
Here we are going to learn about sentence factors (Parts of a Sentence).
A sentence has been usually made up of different types of words and we place these words at their certain places according to their role in that sentence. We call these places as parts of a sentence.
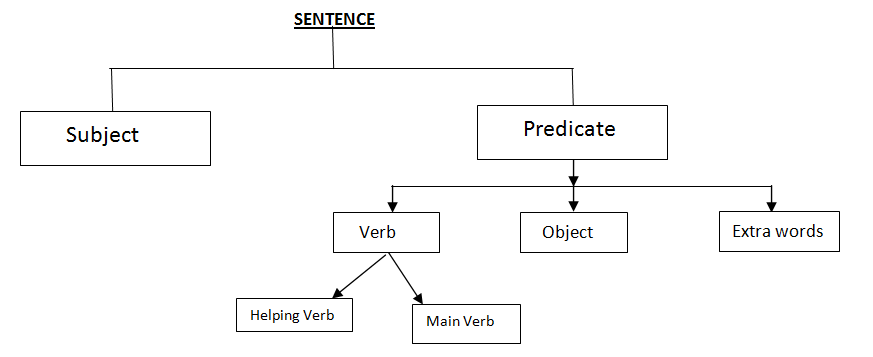
Let us understand these parts one by one:
- A subject: A subject is a part of the sentence which tells us who we talk about. In a sentence doer of the action or the noun/pronoun which we talk about is called a sentence.
Examples:
- Hari is waiting for the bus. (ask….who is waiting….?)
- My father is an army man. (ask…who is an army man…?)
- India’s president will deliver a speech. (ask…who will deliver…?)
- This car runs very fast.
In above four examples, we can see clearly that “Hari, my father, India’s president, and this car” tell us about the doer of action or the person or a thing we talk about. They all called a subject in their respective sentences.
- A predicate: A predicate, in a sentence, is a part of the sentence without subject.
In the above examples, if we remove subjects, the remaining part of the sentences is called a predicate.
Example: Hari is waiting for the bus.
Here the underlined part, without subject, is the predicate for this sentence.
A predicate has the following sub-parts:
- A verb: A verb, in a sentence, is a part of the sentence which tells us about the action and the time of the action (Present,Past or Future)
There are two types of verbs:
Helping Verb: This tells you the tine of action in a sentence.
Example: He was writing a letter to his father. (here ‘Was’ shows past tense)
Main verb: This tells you about the action takes place in the sentence.
Example: I am typing an e-mail. (her the word ‘typing’ shows action)
- An object: in a sentence, an object is a noun or pronoun that receives the action done by the subject or that comes after subject. In a sentence, there may be more than one object.
- Examples: Hari is waiting for the bus. (ask….who is waiting….?)
- My father is an army man. (ask…who is an army man…?)
- India’s president will deliver a speech. (ask…who will deliver…?)
- This car runs very fast.
In the above examples, the underlined words are objects for their respective sentences.
- Extra words: In a sentence, after selecting the subject, verb(helping and main verb) and objects, all the other words are extra words for that sentence.
Example:
My grandfather was living in Indore before last year.
(My grandfather- subject
Was– helping verb
Living– action
In Indore– object
Before last year- extra words.)
In the next lesson, we will learn how to place these parts of sentences to make a meaningful sentence. We will also learn the structures of different types of sentences and how to interchange one type of sentences into another one.

